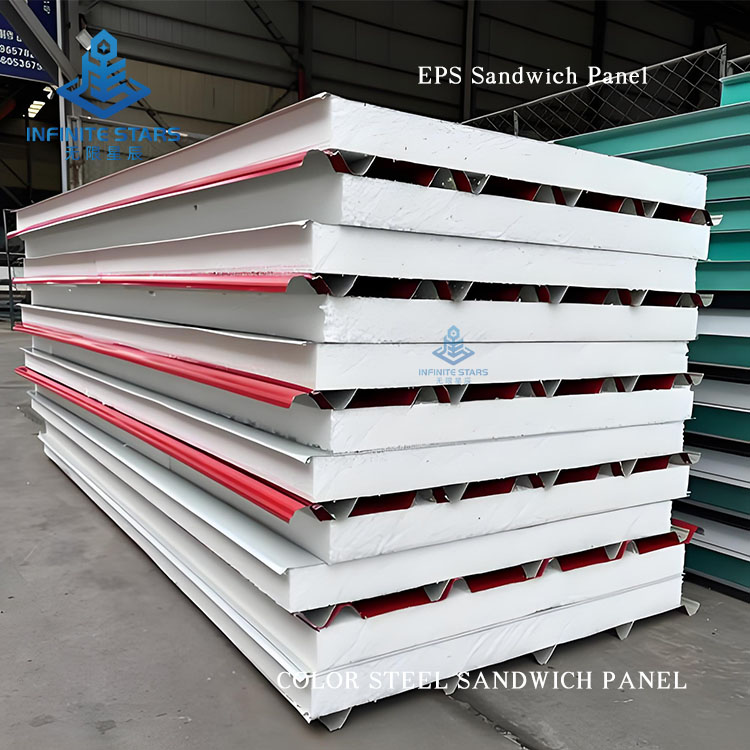
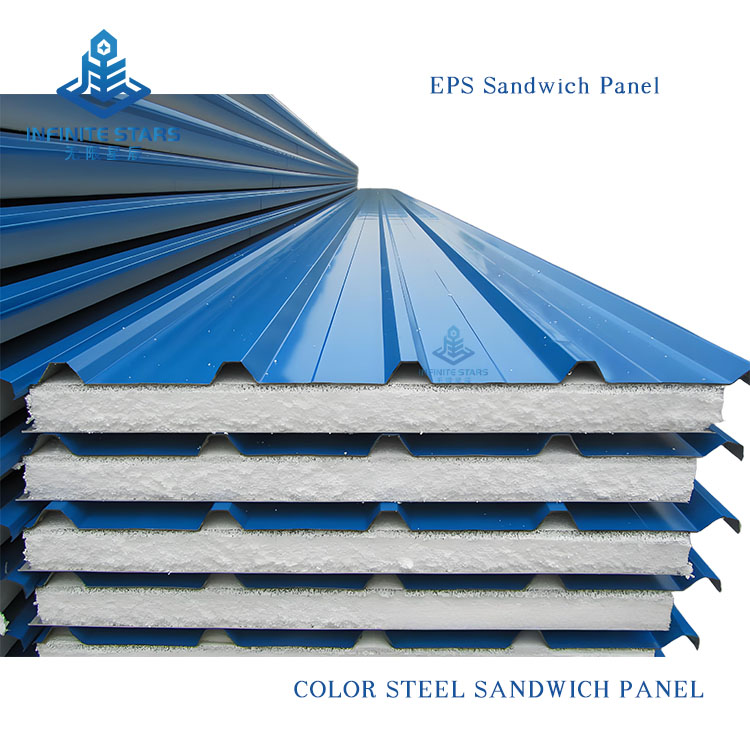
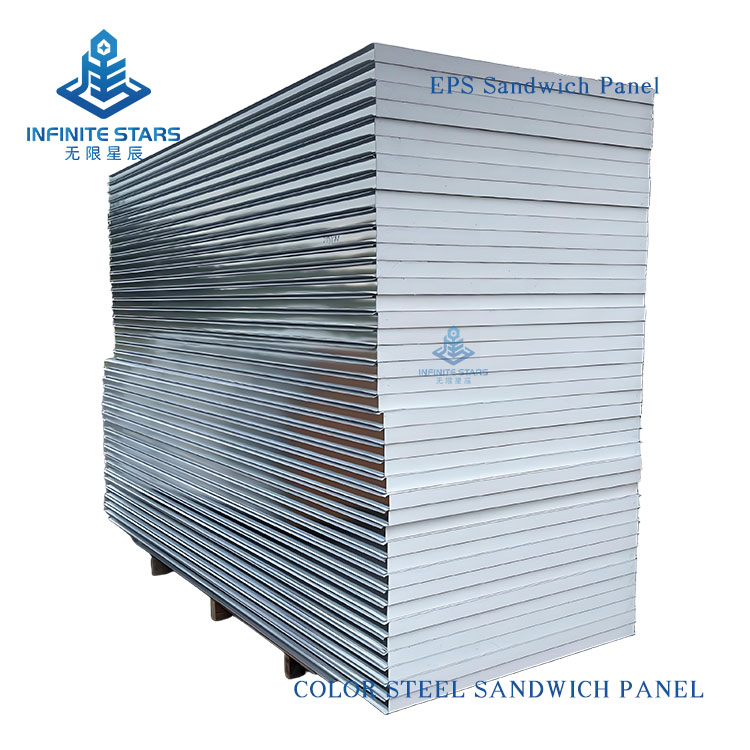
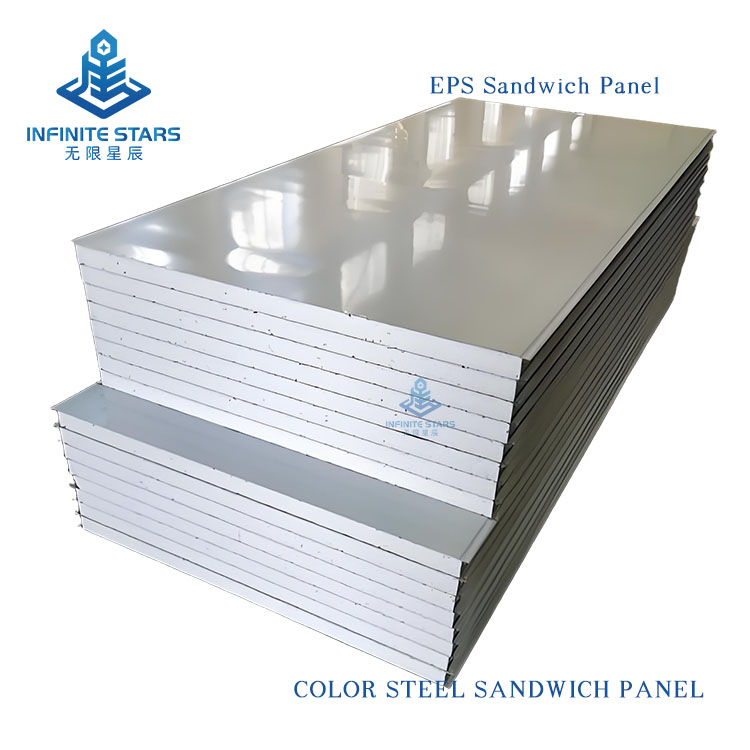
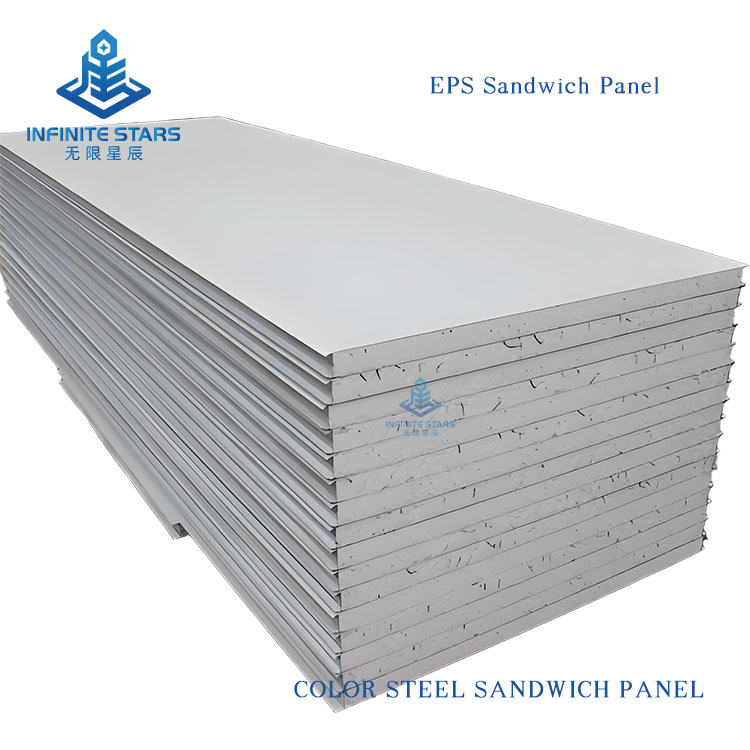
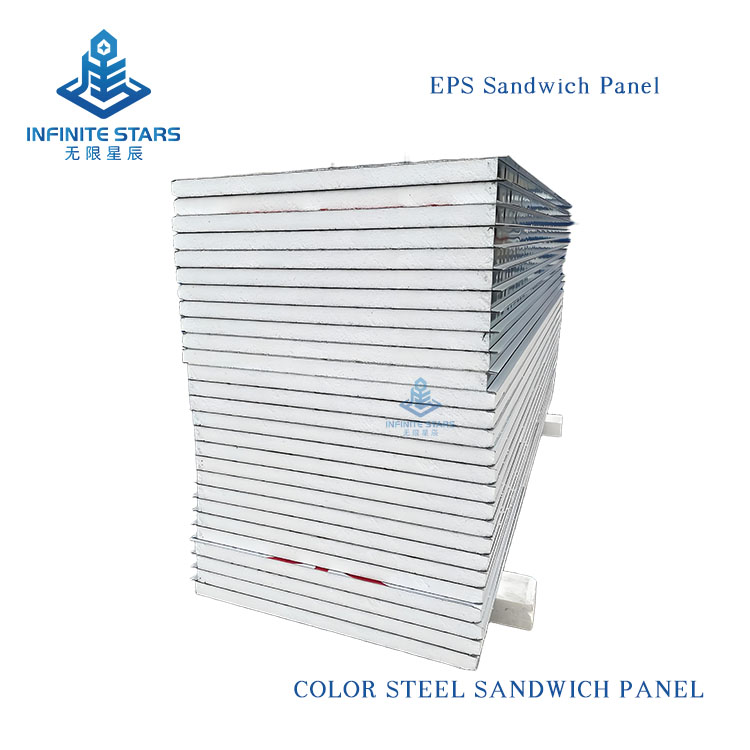
Introduction to EPS Sandwich Panels
EPS sandwich panels (also known as polystyrene sandwich panels) are a common type of lightweight composite board, consisting of two outer metal (or non-metal) facings and a core of expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam bonded together with adhesive. Below is a detailed introduction to EPS sandwich panels.
1. Structure
Outer Layers: Typically made of color-coated steel, aluminum, stainless steel, or fiber cement boards, providing strength and protection.
Core Material: EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), a lightweight foam plastic with a closed-cell structure, offering excellent thermal insulation.
Adhesive: High-strength glue bonds the facings to the core, ensuring structural stability.
2. Key Features
Lightweight & Strong: Low density (core density usually 12-20 kg/m³), easy to transport and install, yet with good load-bearing capacity.
Thermal Insulation: Low thermal conductivity (~0.035-0.045 W/(m·K)), ideal for temperature-controlled environments.
Fire Resistance: Standard EPS is B1/B2 flame-retardant (with fire retardants); fire rating can be improved with facing materials.
Waterproof & Moisture-Resistant: Closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, suitable for humid conditions.
Cost-Effective: More affordable than rock wool or polyurethane (PU) sandwich panels.
Easy Installation: Can be cut, drilled, and installed quickly, commonly used in modular construction.
3. Applications
Construction Industry:
Walls, roofs (e.g., factories, warehouses, cold storage, prefab houses).
Temporary structures (site offices, sales centers).
Interior Decoration: Partitions, ceilings, etc.
Other Uses: Advertising boards, HVAC ducts, etc.
4. Pros & Cons
Advantages:
Lightweight, reducing structural load.
Excellent thermal insulation, improving energy efficiency.
Good sound insulation (especially for mid-low frequency noise).
Corrosion-resistant, long service life (15-30 years).
Disadvantages:
Standard EPS is flammable; fire retardants are required for safety.
Lower compressive strength than PU or rock wool panels, unsuitable for heavy-load applications.
UV exposure may cause aging over time, requiring protective coatings.
5. Comparison with Other Sandwich Panels
| Type | EPS Sandwich Panel | Rock Wool Sandwich Panel | Polyurethane (PU) Sandwich Panel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | EPS Foam | Mineral Wool | Polyurethane Foam |
| Fireproof | B1/B2 | A1 (Non-combustible) | B1 (Flame-retardant) |
| Insulation | Excellent | Moderate | Superior |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High |
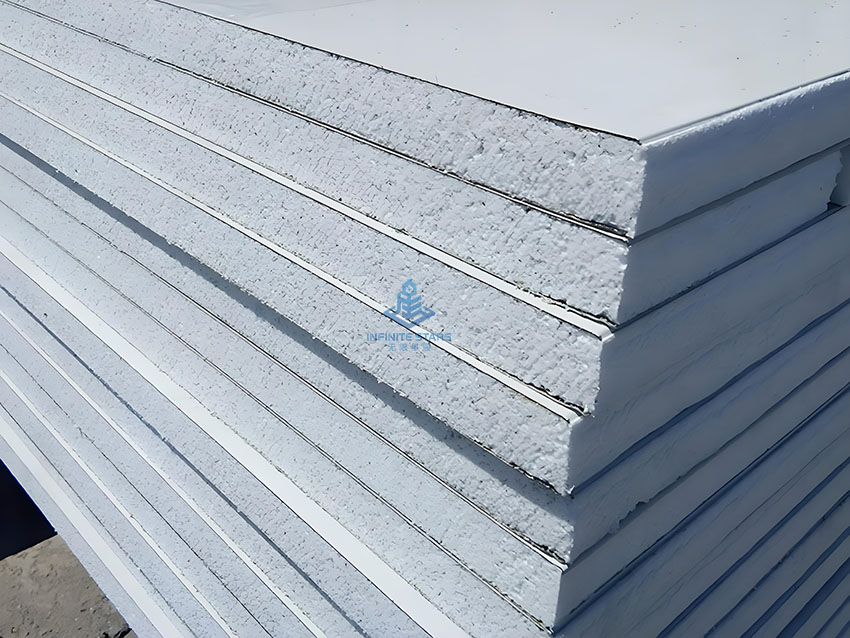

6. Considerations
Fire Safety: Use with caution in high-rise buildings or crowded spaces; opt for fire-resistant versions if needed.
Installation: Seal joints properly to avoid thermal bridging.
Eco-Friendliness: EPS is recyclable but slow to degrade; proper disposal is necessary.
EPS sandwich panels are widely used in industrial and civil construction due to their cost-effectiveness and functionality. However, selecting the right type based on fire resistance, strength, and other requirements is essential.