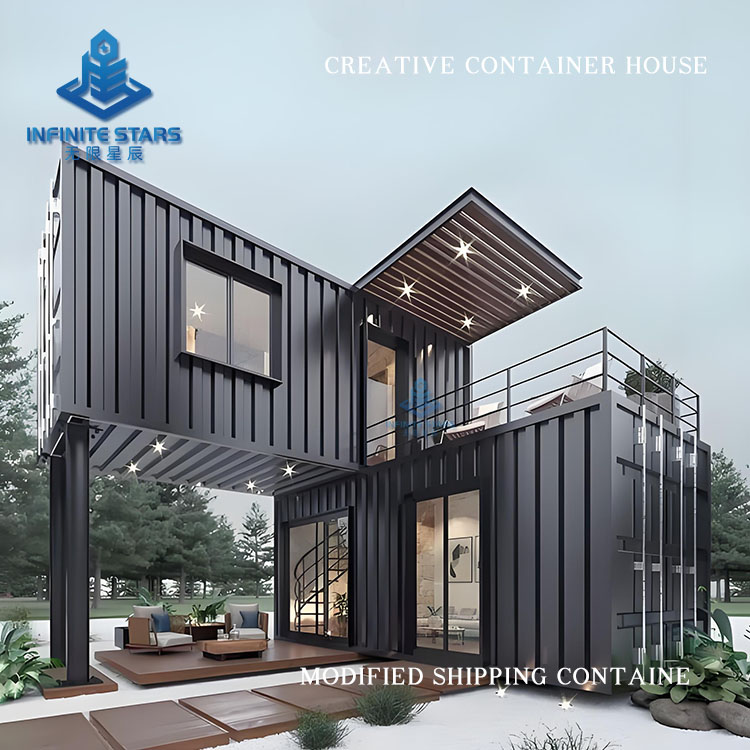
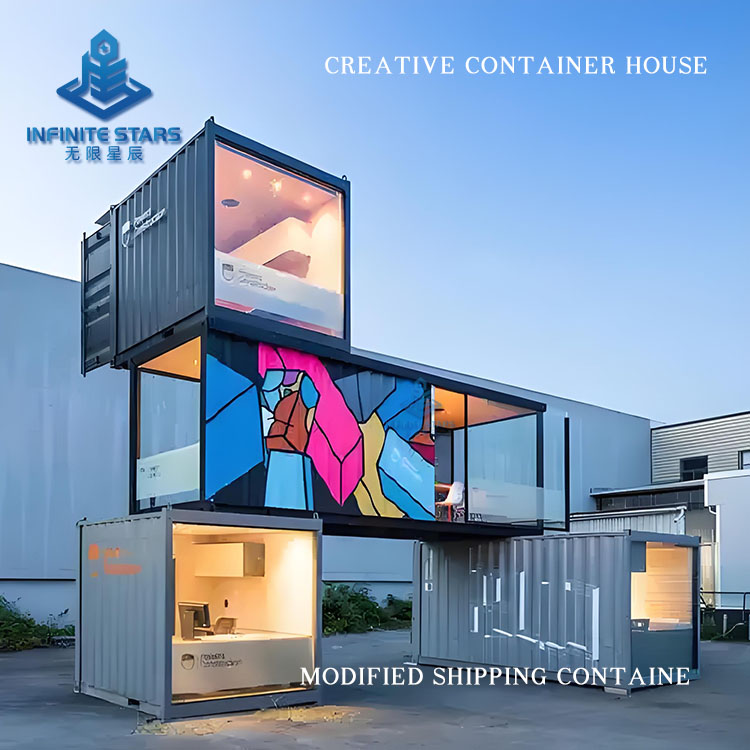
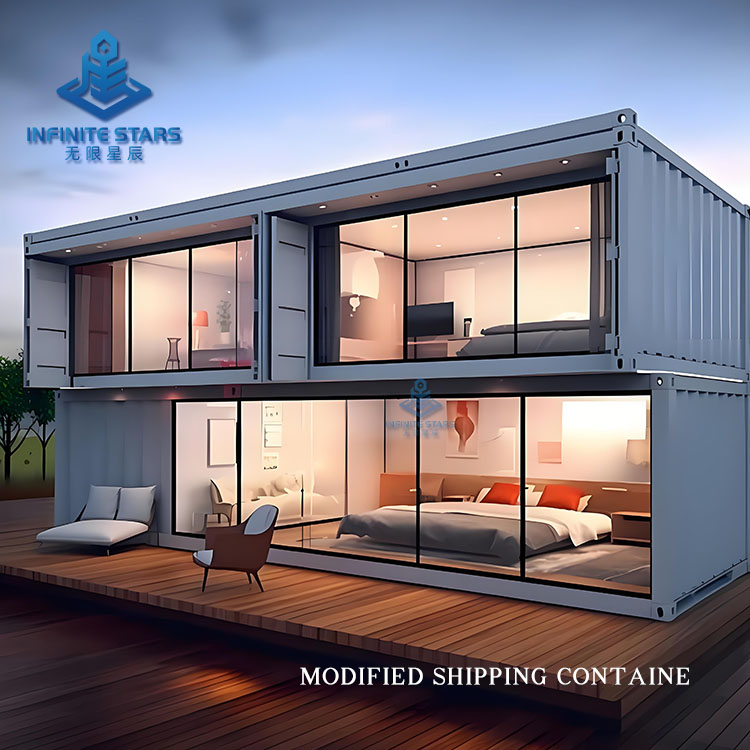
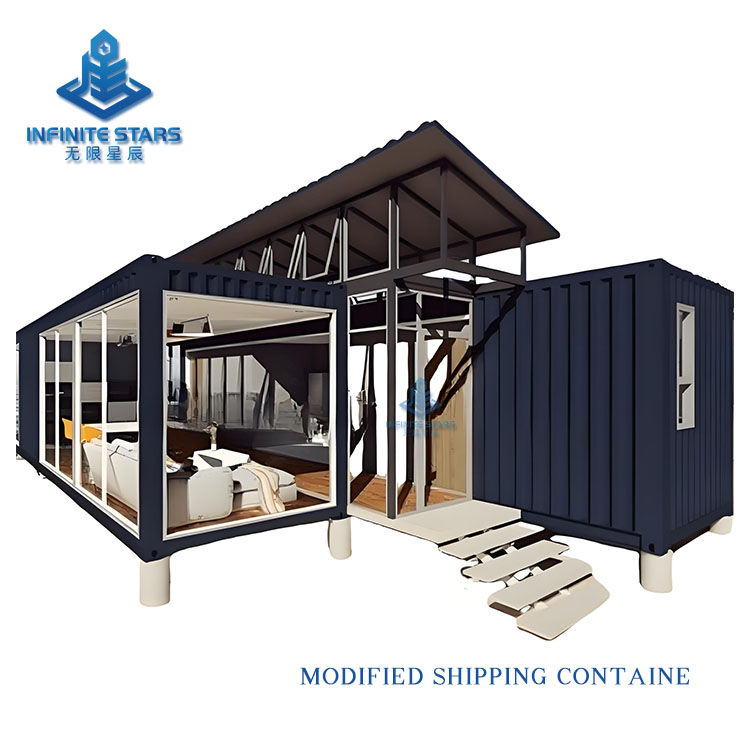
Introduction to Shipping Container Homes
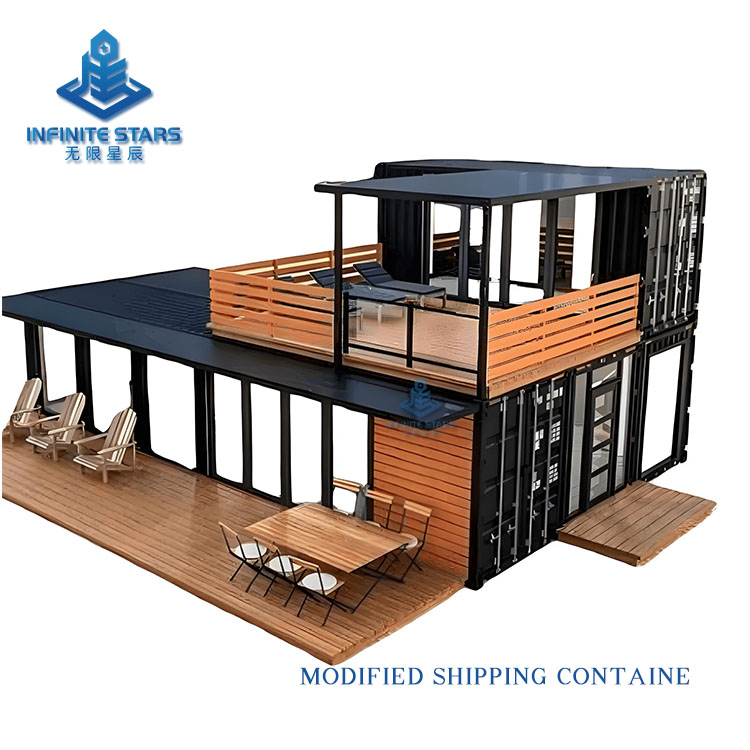
Shipping container homes are an innovative architectural form that involves transforming retired or unused containers into functional living or commercial spaces through design, cutting, reinforcement, and renovation. This construction method has gained global popularity in recent years due to its eco-friendliness, affordability, and flexibility. Below is a detailed introduction to shipping container homes.
1. Core Advantages of Container Homes
Eco-Friendly & Sustainable
Repurposes discarded containers, reducing steel waste and construction debris.
Lower carbon emissions during construction compared to traditional buildings.
Cost-Effective
Low material costs: Used containers typically cost 30%-50% less than new ones.
Short construction period (30%-70% faster), significantly reducing labor and time expenses.
Flexibility & Modularity
Containers can be combined freely to create various layouts (e.g., single-unit studios, multi-unit villas, commercial complexes).
Easy to transport and relocate, ideal for temporary or mobile needs.
Durable & Sturdy Structure
Steel frames resist wind and earthquakes (withstands Category 12 typhoons and magnitude 8 earthquakes).
With anti-corrosion treatment, lifespan reaches 20-30 years.
2. Key Renovation Techniques
Structural Modifications
Cutting Openings: Doors and windows must be installed while preserving load-bearing structures (laser cutting ensures precision).
Reinforcement: Additional steel columns or internal frames are needed for multi-level stacking.
Insulation & Temperature Control
Spray polyurethane foam or fill with rock wool (typical thickness: 5-10 cm).
Double-glazed windows + external shading improve energy efficiency.
Rust & Corrosion Prevention
Sandblasting + epoxy zinc-rich primer + polyurethane topcoat.
Coastal areas may require galvanized steel or aluminum cladding.
Interior Design
Light steel stud walls save space; SPC vinyl flooring is commonly used.
Electrical and plumbing systems are pre-installed in walls or raised floors.
3. Common Applications
| Type | Examples | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | Micro-apartments, family villas | Built-in bathrooms/kitchens, loft designs for space efficiency |
| Commercial | Cafés, pop-up stores, offices | Industrial aesthetics, low-cost rapid setup |
| Public Use | Mobile hospitals, schools, disaster relief housing | Quick deployment, solar/water recycling systems |
| Creative | Art studios, vacation rentals | Custom cuts + glass facades for unique designs |
4. Cost Estimate (20ft Standard Container)
| Item | Basic (USD) | Premium (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Container | 2,500 | 5,000 (new) |
| Structural Work | 1,800 | $3,000+ (custom cuts) |
| Insulation & Finishing | 5,000 | 12,000 (smart systems) |
| Total (per unit) | 10,000 | 25,000 |
Note: Costs vary by region, materials, and design complexity.
5. Key Considerations
Legal Compliance
Most countries require temporary building permits; some prohibit long-term residency.
Must meet fire safety (e.g., BS476) and seismic codes.
Living Comfort
Install ventilation systems; remove container flooring (with structural compensation) for higher ceilings.
Northern climates recommend underfloor heating + triple insulation.
Transport & Installation
Maximum transport height for a 40ft container: ~4m (including trailer).
Mountainous areas require concrete foundations or screw pile supports.
6. Future Trends
Smart Integration: Prefabricated modules with solar roofs and rainwater recycling.
Vertical Expansion: Singapore’s 18-story container apartments (HDB project).
3D Printing: Printed interior components for faster customization.
With thoughtful design, shipping container homes can match the comfort of traditional houses, making them ideal for personalized, short-term, or budget-conscious projects. Before starting a renovation, consult a professional container architecture firm to ensure safety and functionality.